Advancements in Battery Technology
China’s HiNA, in collaboration with JAC and Volkswagen, unveiled the iEVA50, the world’s first electric car equipped with a sodium-ion battery. Mass production of sodium-ion battery-powered vehicles is slated to begin in 2023, with other Chinese manufacturers like CATL and BYD joining the race. With over 100 GWh of production capacity in the pipeline, mainly in China, the industry is rapidly embracing this promising technology.
To truly compete on a global scale, sodium-ion batteries must demonstrate their ability to meet the demands for EV range and charging time. As a result, some companies are initially targeting less demanding applications, such as stationary storage or micromobility. This pragmatic approach allows for gradual exploration of the technology’s capabilities and lays the groundwork for future advancements.
Meanwhile, the resurgence of improved LFP cathodes, known as LFP 2.0, is transforming the EV market. LFP batteries are gaining traction in the light-duty vehicle segment, previously dominated by more energy-dense chemistries like NMC and NCA. Recent advancements in LFP chemistry and manufacturing have significantly boosted battery performance, driving substantial growth in market share.
Major automakers, including Tesla, Ford, and Volkswagen, are keen to incorporate LFP batteries into their electric vehicles, indicating a shift in industry preferences toward this cost-effective and efficient technology. Moreover, a lithium-manganese-iron-phosphate variant of LFP batteries promises even higher energy density, with mass production expected to commence in 2024.
Innovations in battery anodes are equally essential for overall performance. Doping graphite anodes with silicon has proven transformative, significantly increasing energy density and charging speeds. Startups like OneD Battery Sciences have partnered with industry giants like General Motors and Sionic Energy to bring silicon-graphite blended anodes to the market in 2023.
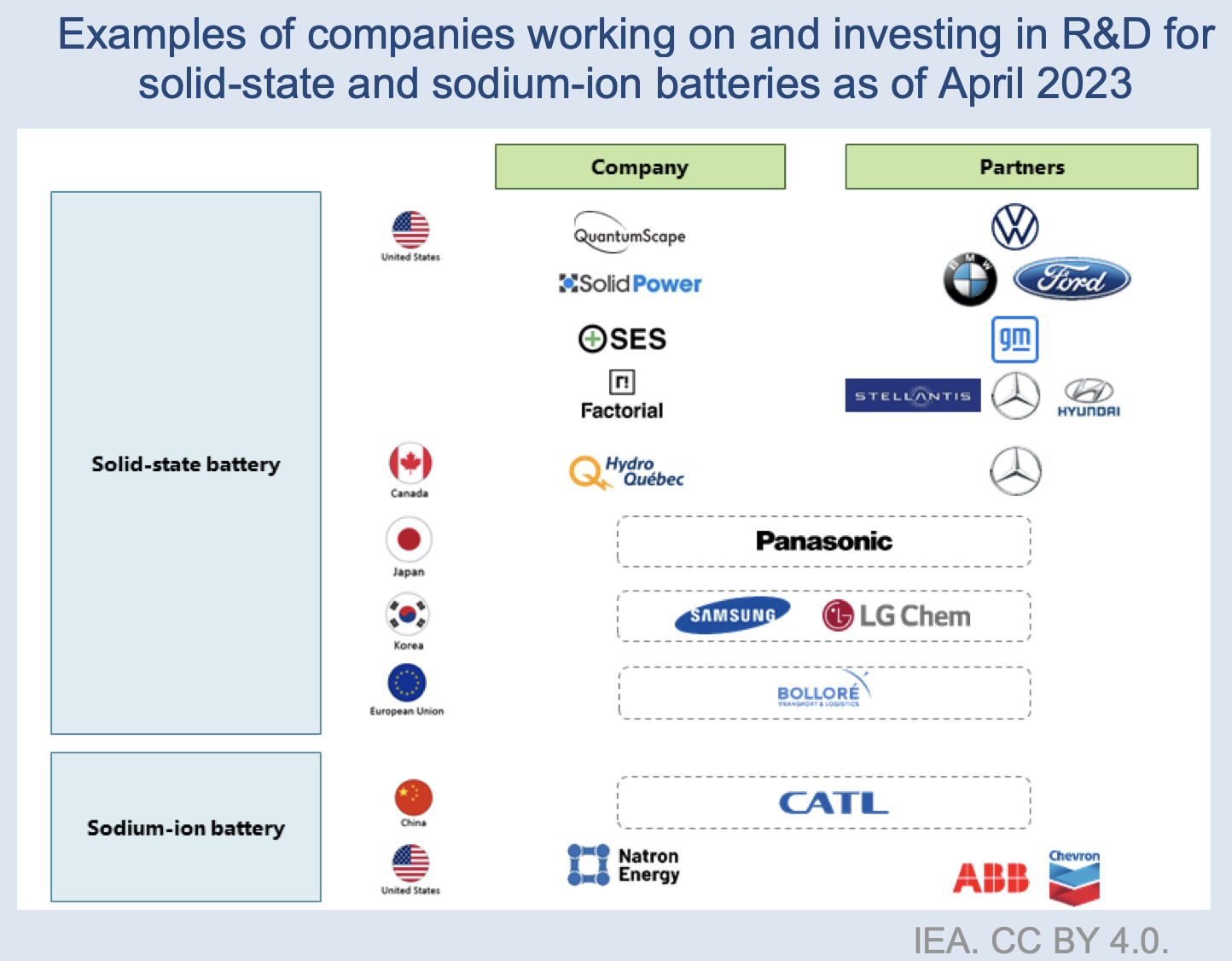
Solid-state batteries represent yet another frontier in battery R&D. By replacing traditional graphite anodes with lithium metal anodes or pure silicon, solid-state batteries offer enhanced energy density and thermal safety. Key players such as QuantumScape, Solid Power, and Factorial Energy, along with major automakers, are driving the development of solid-state batteries, heralding a potential revolution in the electric vehicle industry.
While these advancements show immense promise, long-term potential lies with lithium-sulfur batteries. These batteries have the capacity to surpass existing energy densities and unlock new possibilities for EV range and charging times. However, scaling up lithium-sulfur batteries requires overcoming significant technological challenges.
As battery technologies rapidly evolve, the recycling industry faces new hurdles. Adapting to diverse battery chemistries demands constant innovation, and strong policy support is necessary to ensure the responsible and sustainable recycling of lower-value materials used in emerging batteries.
In conclusion, the ongoing advancements in battery technologies offer exciting prospects for a sustainable future. From sodium-ion and LFP batteries to solid-state and lithium-sulfur batteries, these innovations are poised to revolutionise energy storage and reshape transportation as we know it. By investing in research, embracing cutting-edge technologies, and fostering supportive policies, we can accelerate the transition toward a cleaner and more sustainable world.
Source: Critical Minerals Market Review 2023 | IEA